Learning objectives:
- Electricity flowing through a wire creates a magnetic field.
- An electromagnet can attract or repel a magnet, just like a permanent magnet does.
- The changing current of a speaker causes the magnetic field in the wire to change, pulling and then pushing the wire toward and then away from the magnet.
Special projects:
This lesson was inspired by one of the students who asked if they could make a paper plate speaker. I’m always happy to help a student try something they find interesting. All they have to do is ask.
Here is a link to a video that explains how to make a paper plate speaker:
Paper Plate Speaker – The King of Random
Permanent magnets:
Permanent magnets are the “normal” sort of magnets. A permanent magnet is always magnetic. A refrigerator magnet is a permanent magnet.
Electromagnets:
This video shows a good demonstration of how an electric current creates a magnetic field that goes in a circle around the wire.
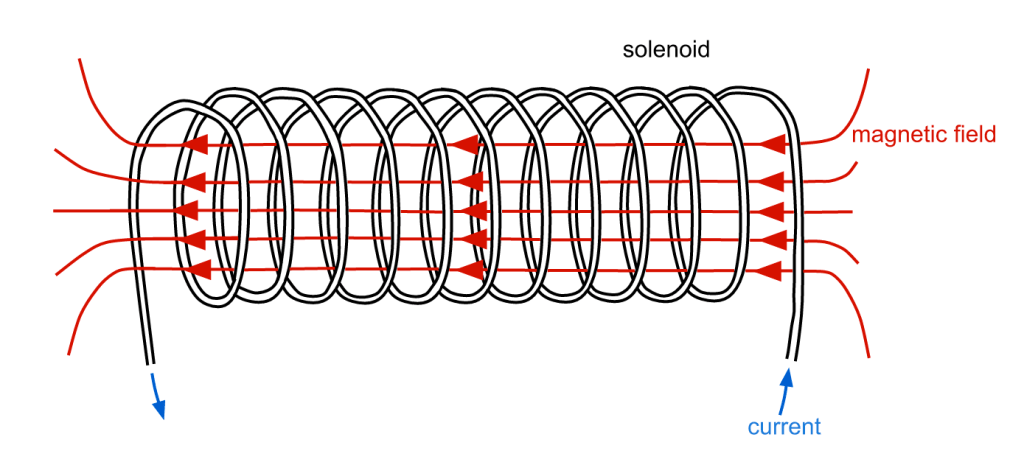
Solenoids:
A solenoid is just a coil of wire that an electric current can move through. The magnetic field inside a solenoid can be strong because all of the small magnetic fields from each loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field in the solenoid.
The magnetic field around a single wire is usually pretty weak, so most electromagnets are in the form of a solenoid.
Motors:
Electric motors use electricity to create a magnetic field that pushes against a magnet, causing the motor to turn.
Here is a video of several types of simple motors:
Leave a comment