Greek and Latin Roots
Here is the list of Greek and Latin roots for this week:
Here is a link to all of the Greek and Latin roots we have discussed.
Assignments
- Fill out the list of Greek and Latin roots.
- Write in the meaning of each root
- Give at least one example of each, be prepared to give its actual definition and the way that it is related to the root word
- Example: If I gave you the root “onym”, you could give the word “synonym” which has the definition of two words with the same meaning. The two roots in the word “syn” and “onym” mean “same name”, indicating two words that name the same thing.
- Fill out the blank space at the bottom with your own root that you have discovered. This will likely come from some of the example words that you have already written. Give a different example than what you have used.
- Example: syn- means “same”, example word “synchronous”
- Be prepared to talk about where you found this information
- Look at this webpage and record the secret code which is “argon“.
- Presentation
- Research your topic of choice and be prepared to give a 5 minute presentation on the topic, geared toward people your age level.
- Include the background information needed for someone who does not know the topic as well as you.
- Be prepared to talk about how you found this information.
Next week we will meet on 7/11/24.
Things We Discussed
Greek and Latin roots
Blood Cell Lines
We discussed the Greek and Latin roots from last week, focusing on:
- erythro- meaning “red”
- leuko- meaning “white”
- thrombo- meaning “clot”
- cyt- meaning “cell”
which combine to give us:
- erythrocyte – red blood cell, which carry oxygen
- leukocyte – white blood cell, which fight infection
- thrombocyte – platelets, which causes blood clots
These are the 3 main cell lines in the blood.
Leukemia
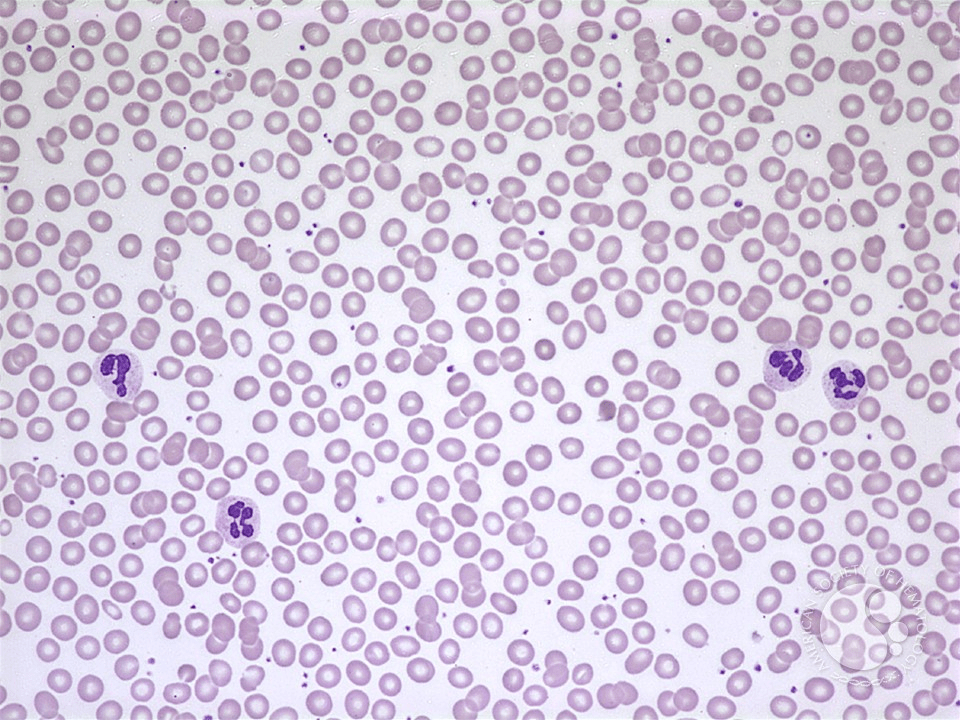
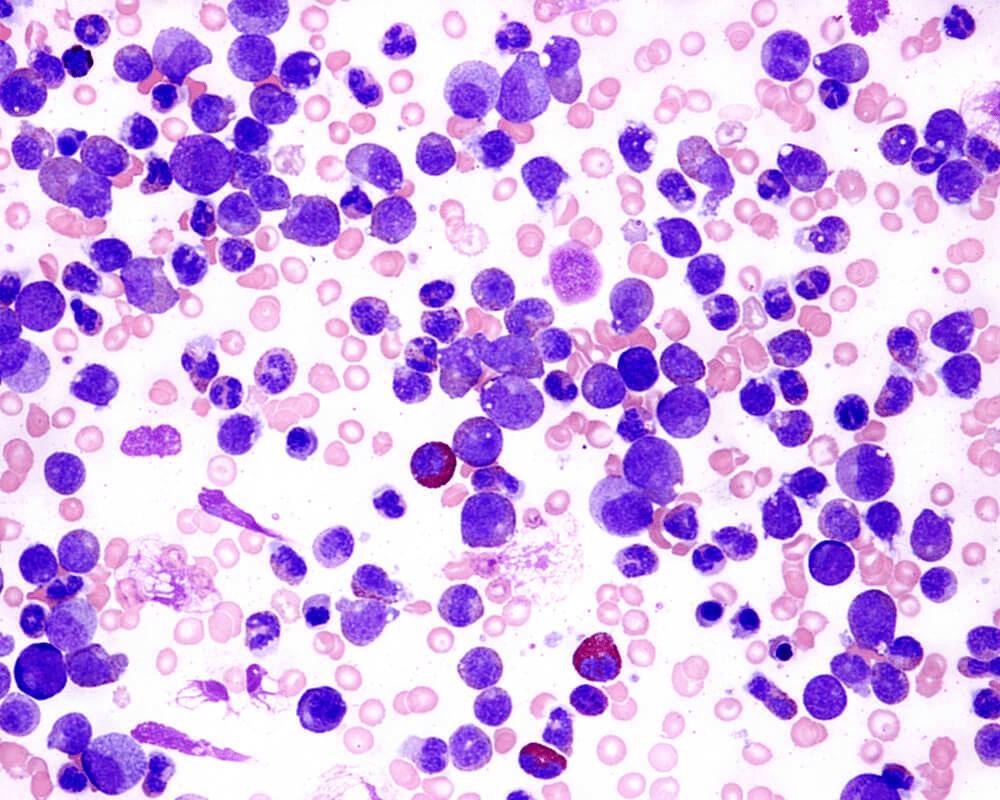
We compared a normal peripheral blood smear with a peripheral blood smear from someone who has leukemia, a type of cancer that causes too many white blood cells.
This is a very useful link for finding Greek and Latin roots:
List of Greek and Latin roots in English – Wikipedia
Organic chemistry
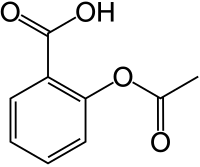
- The structural diagram for aspirin is:
- A carbon atom is represented by the end of a line segment.
- Each carbon atom has 4 bonds. Sometimes a carbon atom with share two bonds with another carbon atom, or with another atom such as oxygen or nitrogen. The total number of bonds for each carbon should always be 4.
- If only 1, 2, or 3 bonds are shown, this means that the other bonds are made with hydrogen.
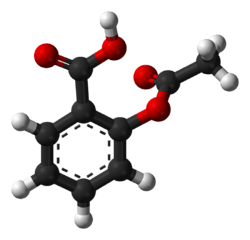
- This is another representation of aspirin. In this image, the carbon and hydrogen atoms are shown.
College 4 Year Plans
- College is typically divided 4 years with 2 semesters in each class.
- A class is only one semester long.
- Credit hours are determined by how many hours a class meets each week.
- Typically, a class will meet 3 days a week (3 credit hours on Monday, Wednesday and Friday) or 5 days a week (5 credit hours).
Example 4 year plans give a student an idea of what classes they will take each year to complete the major, however, there is room for a lot of flexibility.
Here are links to the 4 year plans for some majors at Mizzou:
Breathing
Anatomy
- Airways
- Pharynx
- Epiglottis
- Vocal cords
Vocal Cord Stroboscopy (HD) – YouTube
- Trachea
- Bronchus
- Bronchioles
- Alveolus
- Blood vessels
- Pulmonary arteries
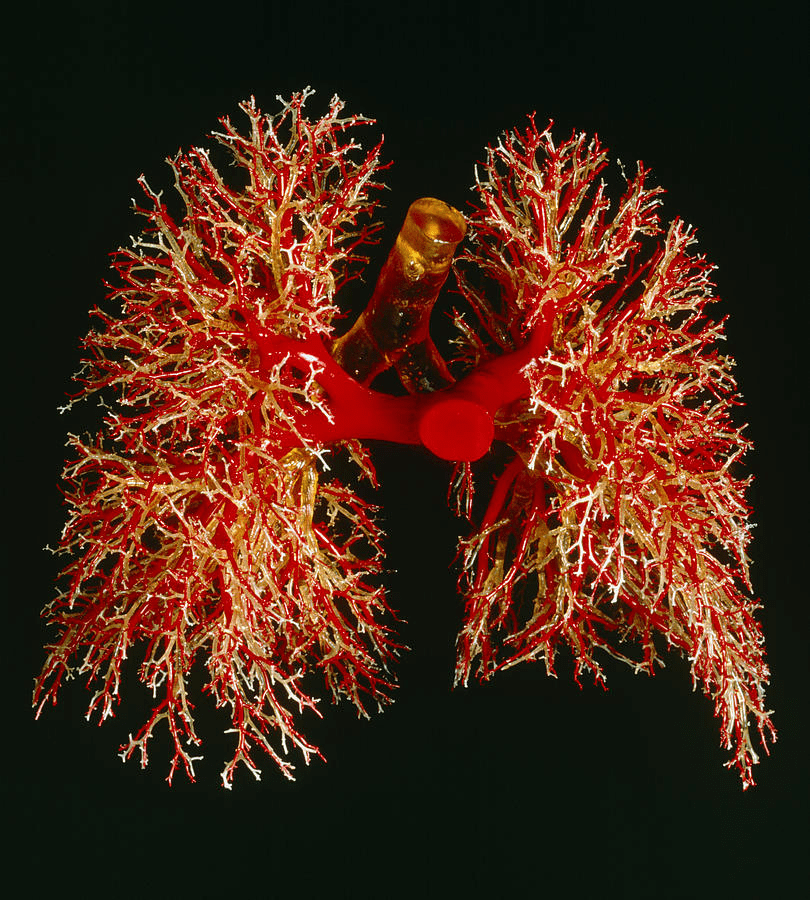
- Pulmonary veins
- Capillaries
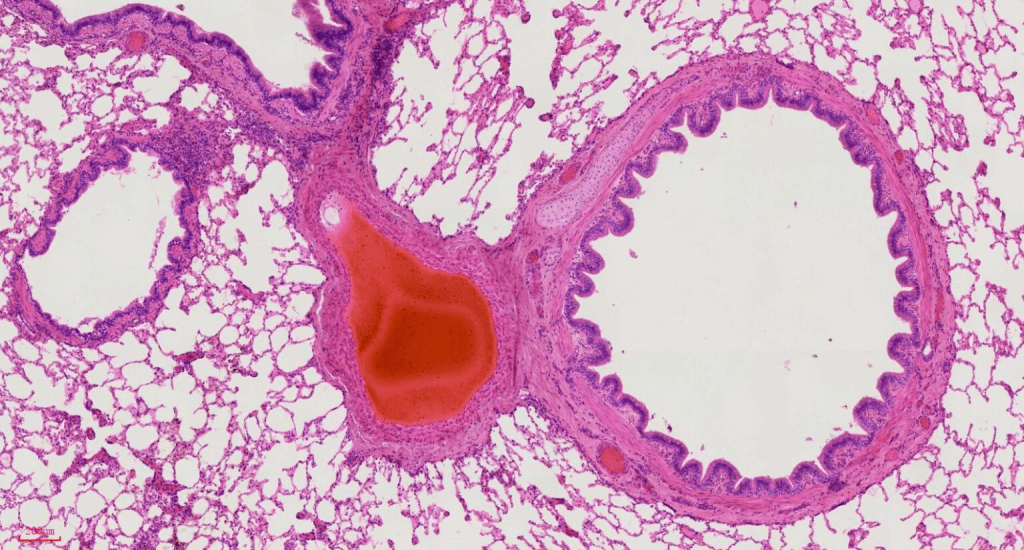
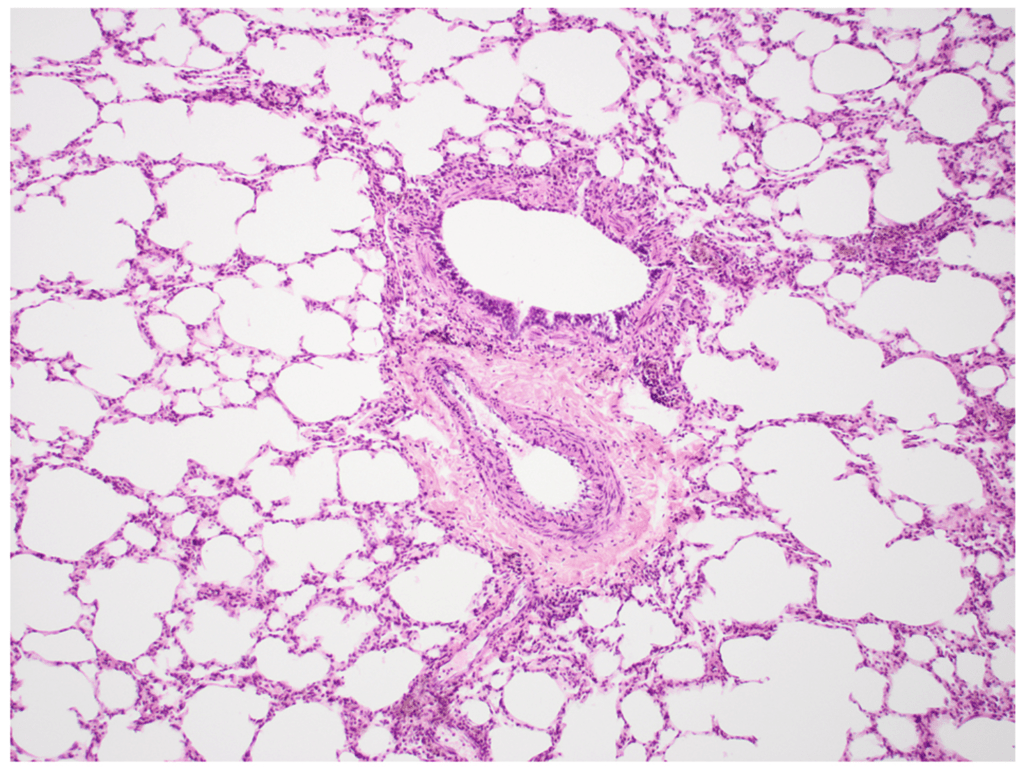
- Muscles and Bones
- chest wall
- diaphragm
Tests
- Chest x-ray

- CT scan
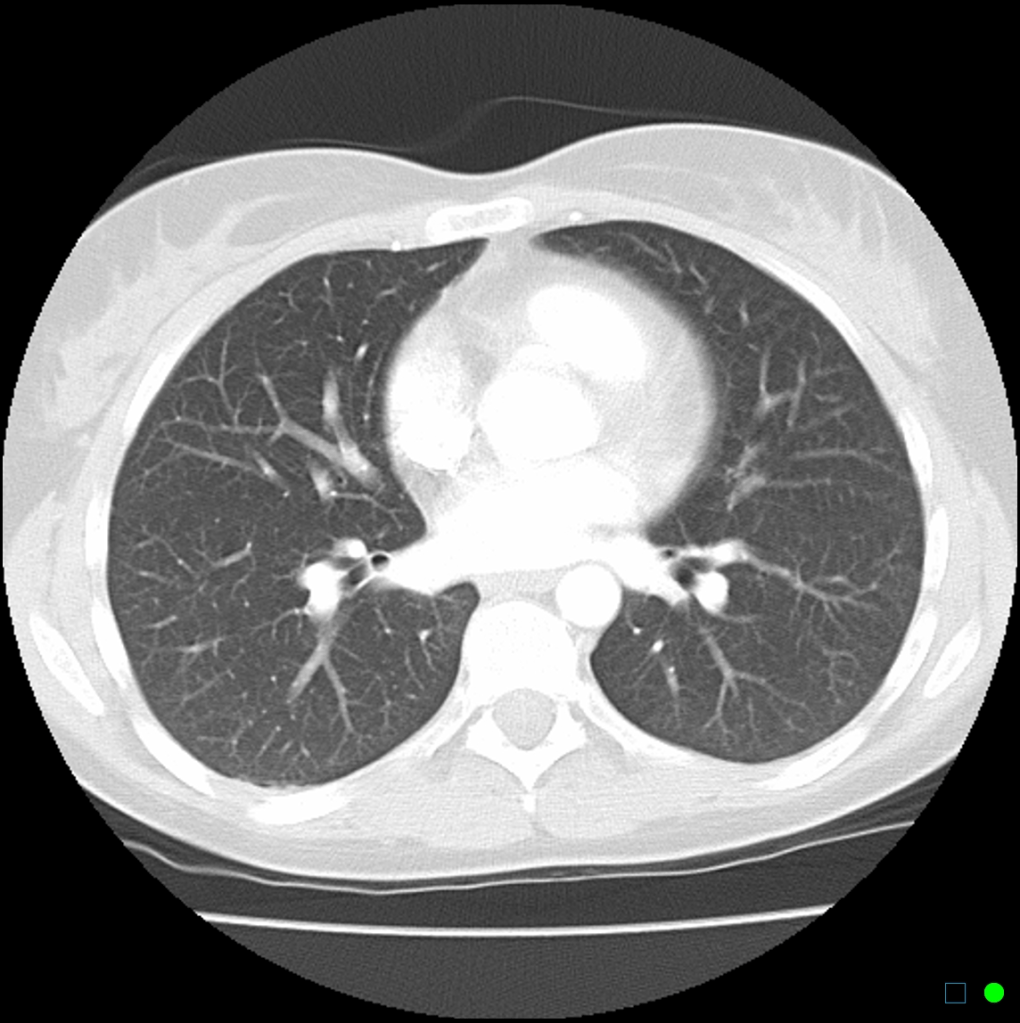
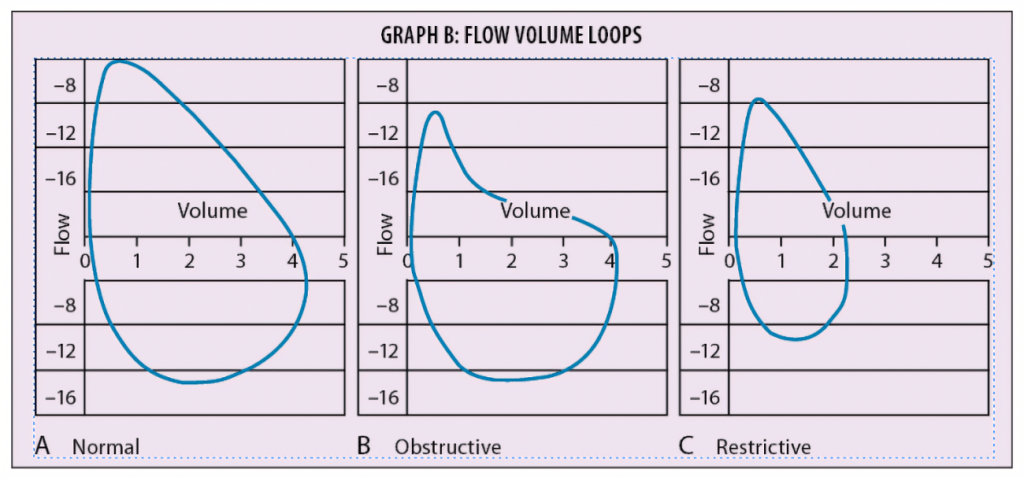
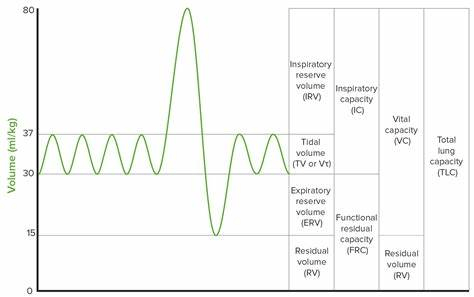
- Pulmonary function tests (PFTs)

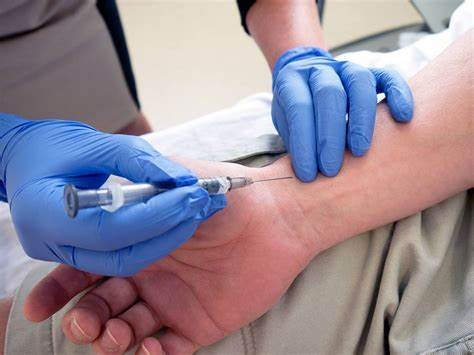
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)
Diseases
- Pneumonia
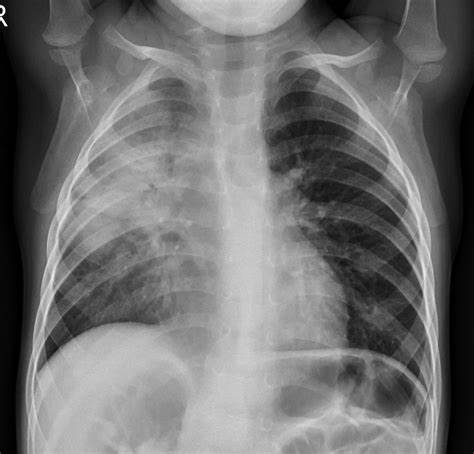
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
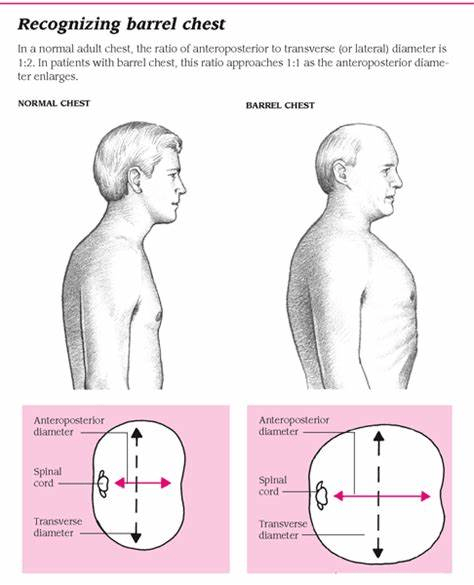
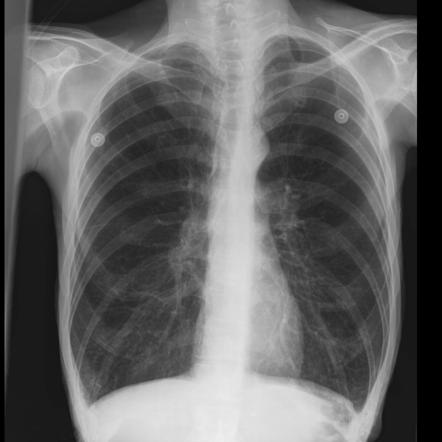
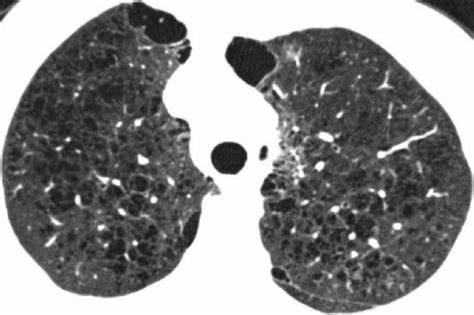
- Restrictive lung disease
- Pneumothorax

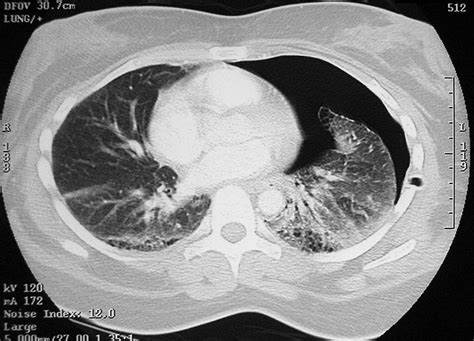
- Pulmonary embolism
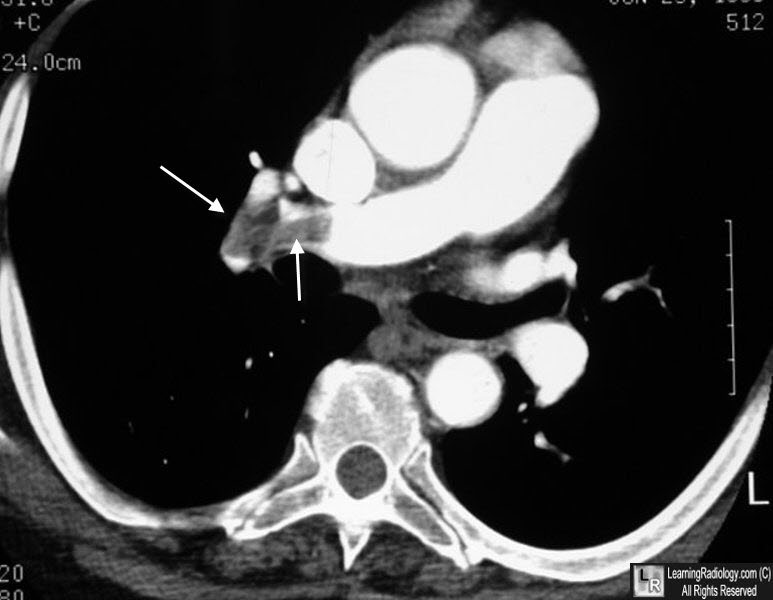
- Congestive heart failure
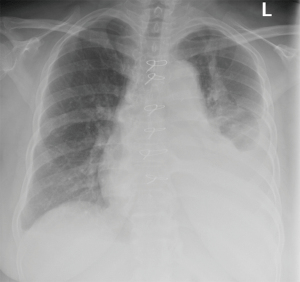
Treatments
- Inhalers
- Nebulizer treatments
- Nasal cannula
- BiPAP
- Ventilator
Intubation & Mechanical Ventilation (Ventilator) (youtube.com)
Electronics
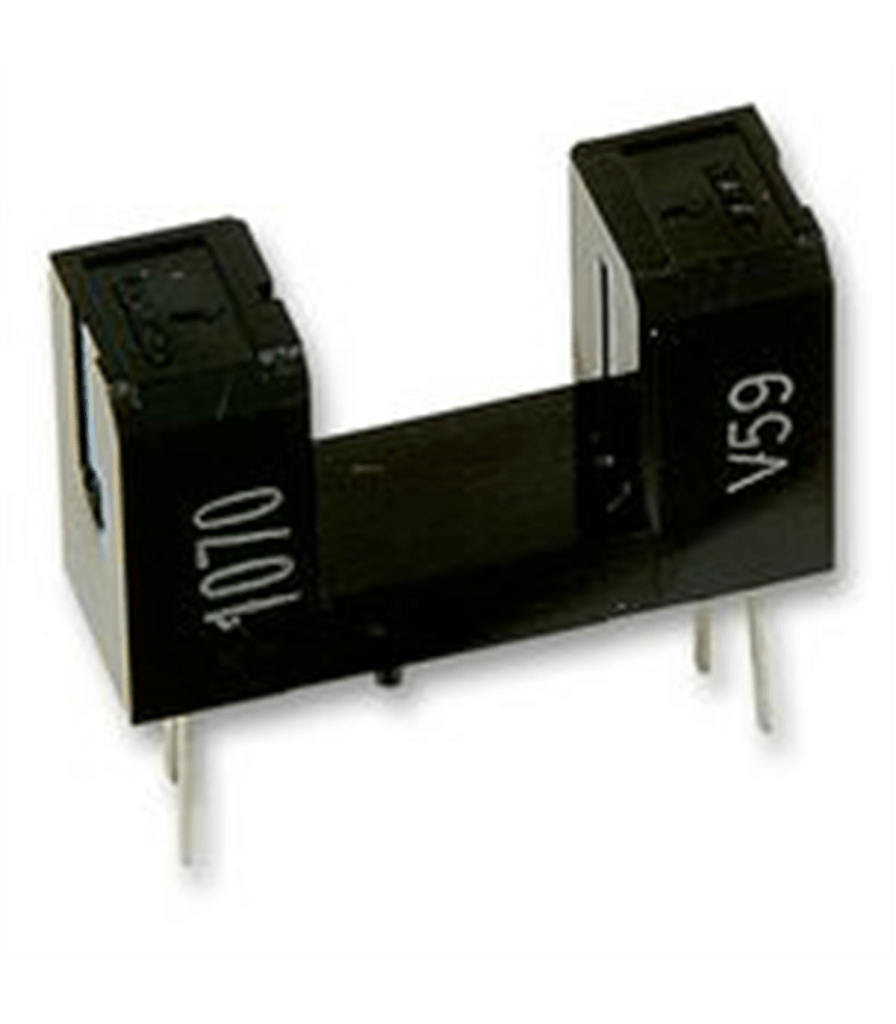
An optical interrupter combines an LED and a sensor into one package. It is used to sense movement.

We looked at this circuit and practiced drawing this circuit diagram and using it to reconstruct the circuit.
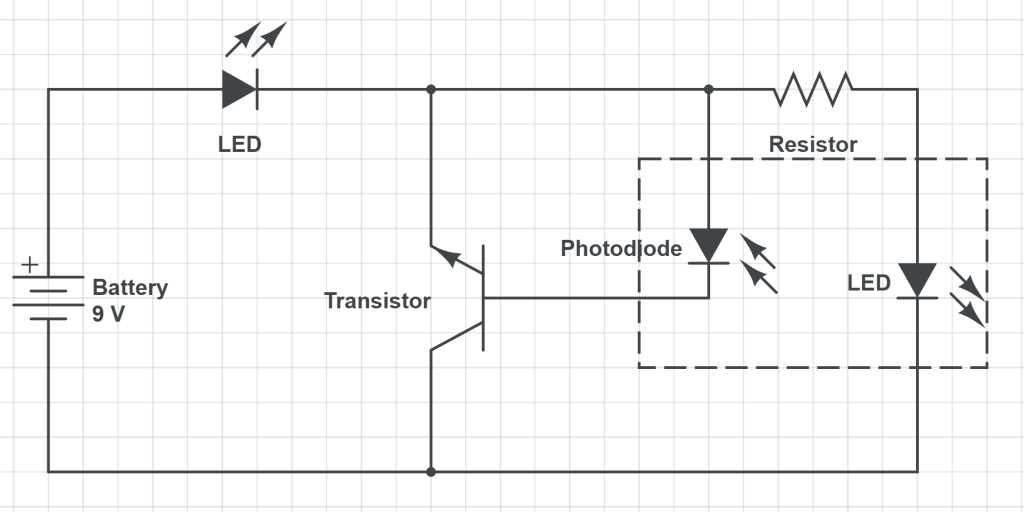
See this link for a list of the electronic components we have discussed and their symbols: Electronic components
Leave a comment