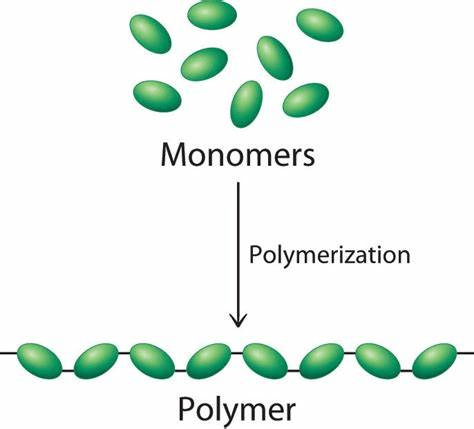
What is a polymer?
- A polymer is a large molecule made up of similar small molecules.
- The small molecules are called monomers.
- Often the monomers in a polymer are identical, but sometimes the monomers are different types of molecules in the same class.
Polymers in biology
- There are 4 classes on polymers that are essential to biology.
| Polymer | Monomer | Uses |
| Protein | Amino acid | Enzymes and structural proteins |
| DNA & RNA | Nucleotide | Contains the information for making proteins |
| Carbohydrate | Monosaccharide | Energy storage |
| Hydrocarbon | -CH2– | Energy storage, cell membrane structure |
Proteins
- There are 20 amino acids that make up all proteins.
- Proteins contain anywhere from a few amino acids to thousands of amino acids.

DNA
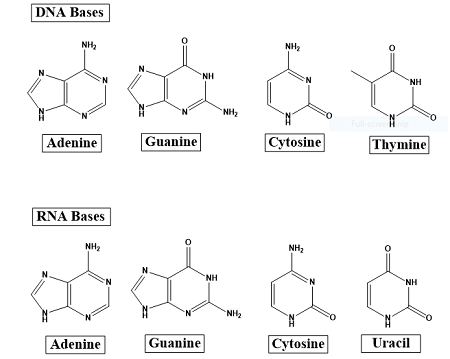
- DNA is made of 4 bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine.
- RNA is also made of 4 bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil.
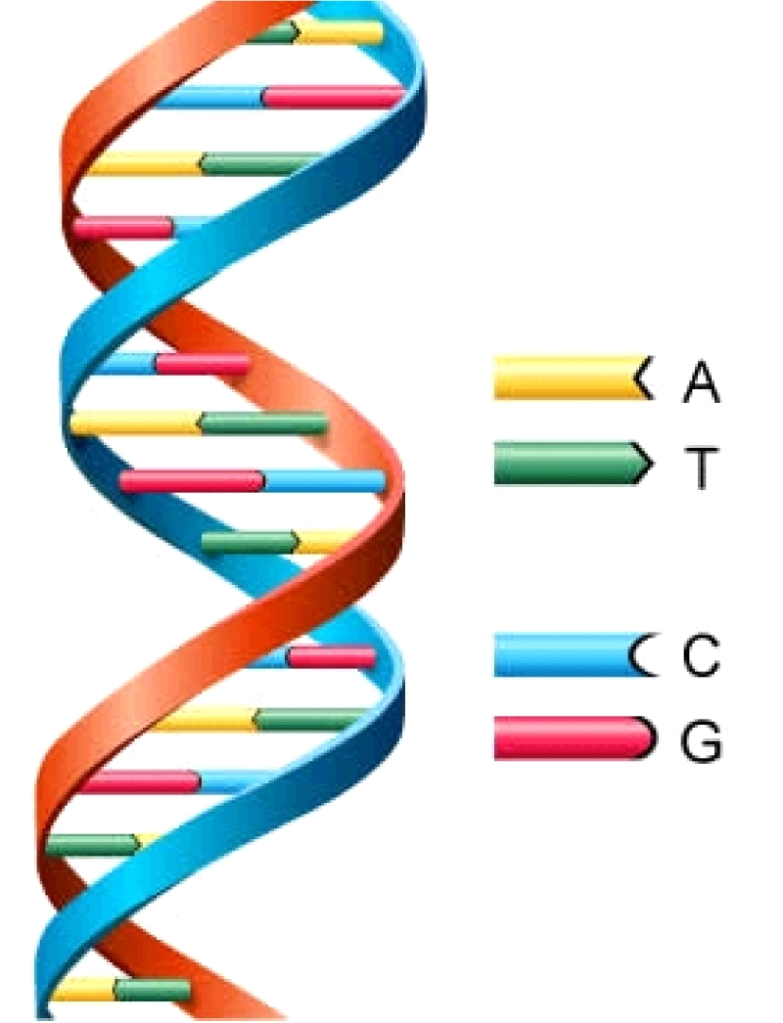
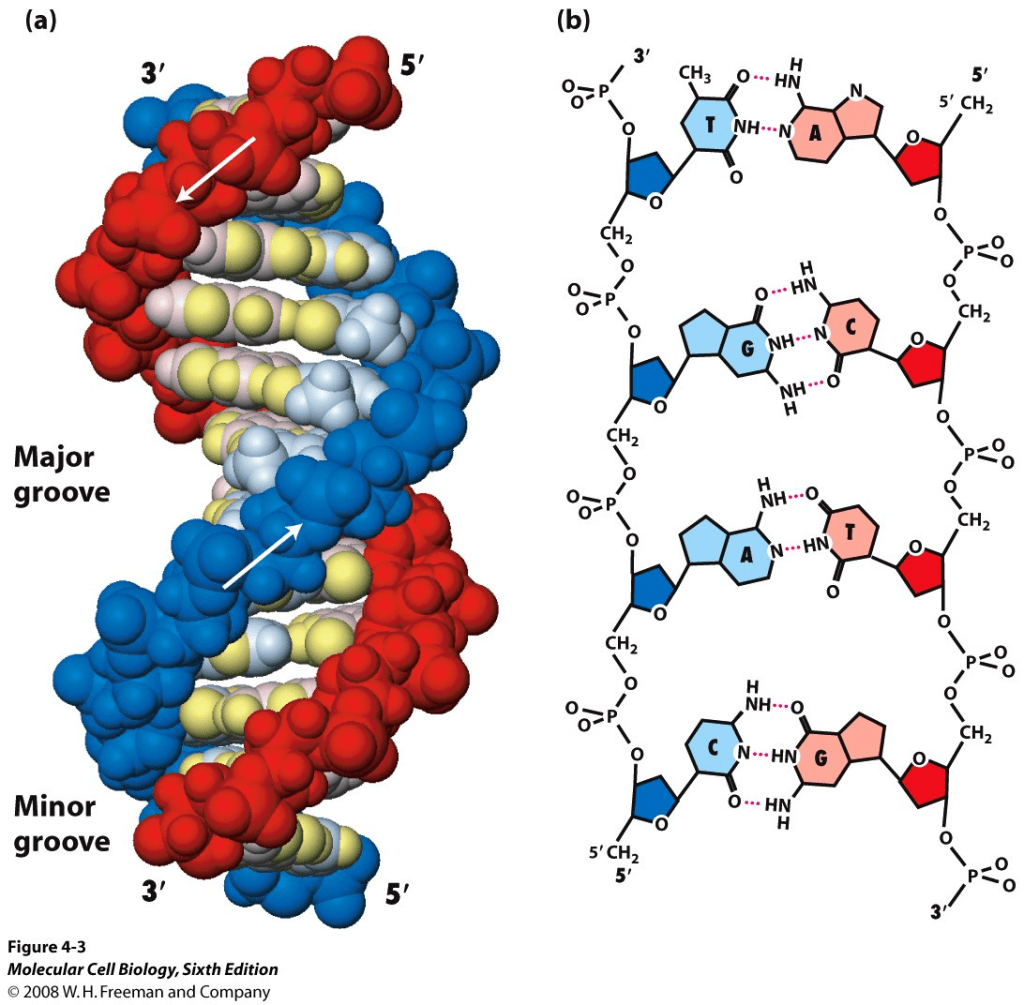
There are many ways to represent the DNA molecule.
Carbohydrates
- Simple sugars are called monosaccharides. These include glucose, fructose, galactose, and ribose (among others).
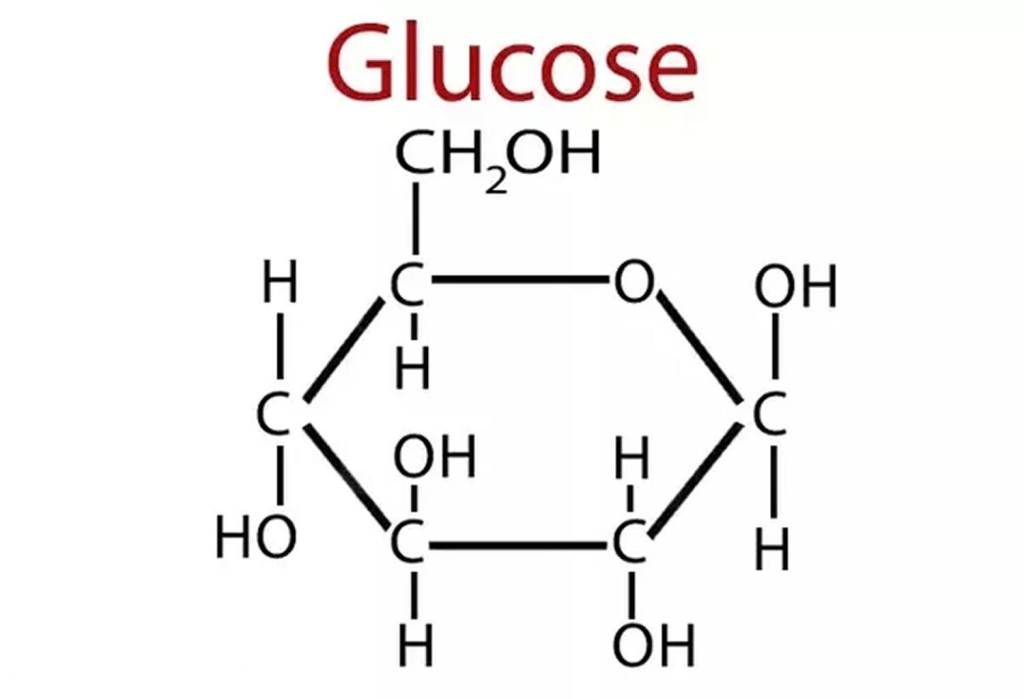
- Two monosaccharides can join to form a disaccharide. Common disaccharides include lactose, sucrose, and maltose (among others).
- Monosaccharides can also join to form polysaccharides, such as starch, glycogen and cellulose.
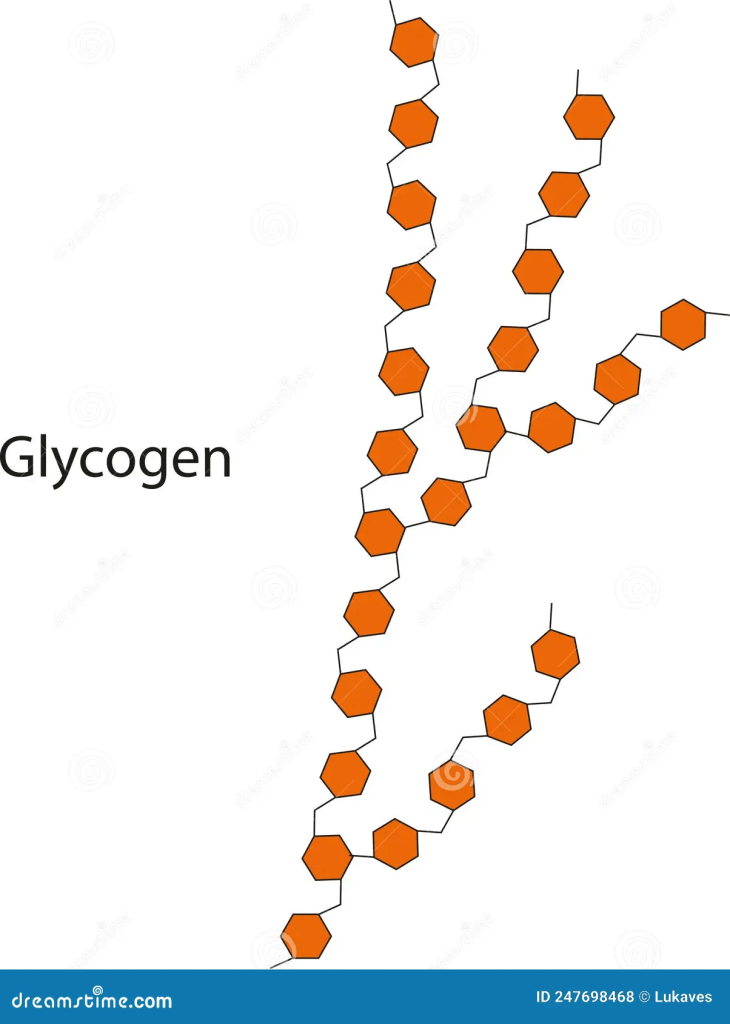
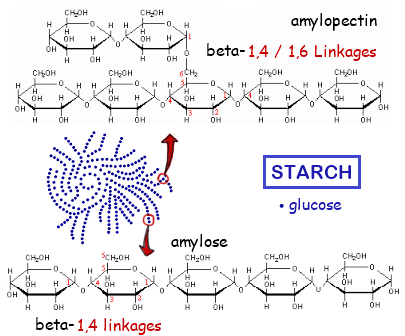
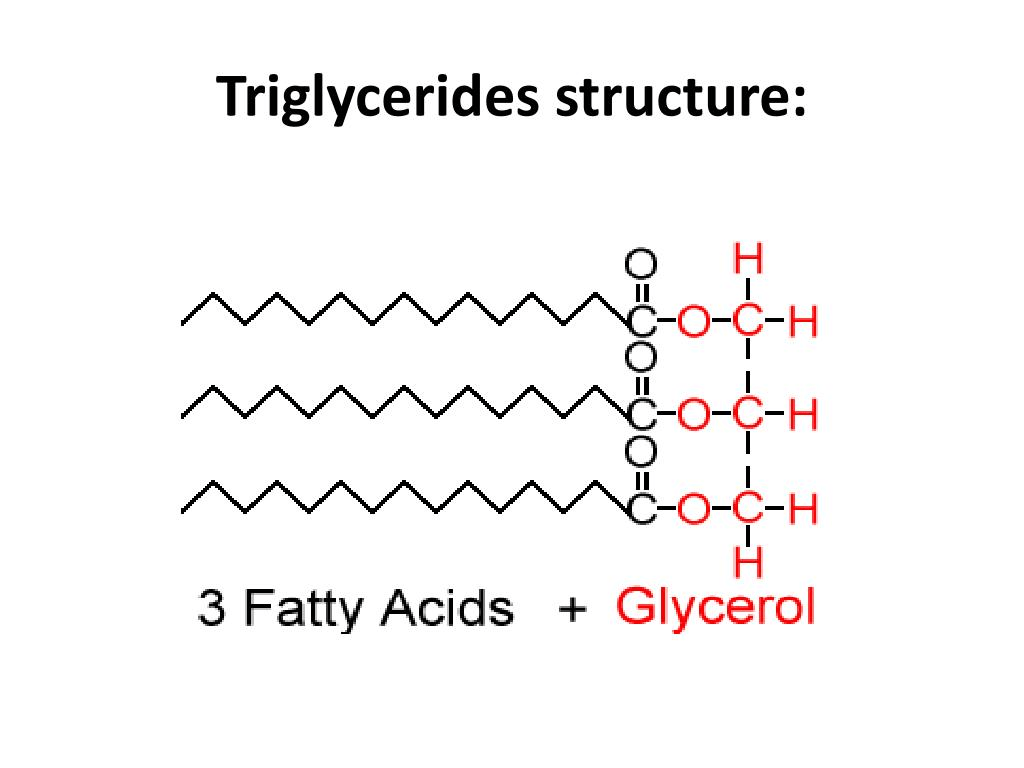
Hydrocarbons
- Hydrocarbons typically contain only carbon and hydrogen.
- By adding a carboxyl group (-COOH) at the end, this becomes what is known as a fatty acid.
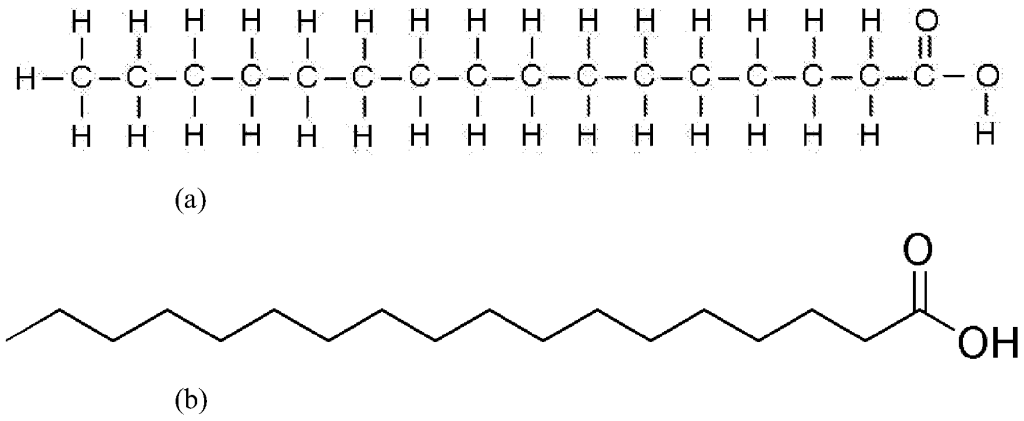
- Fatty acids can, in turn, be joined together to form a triglyceride.
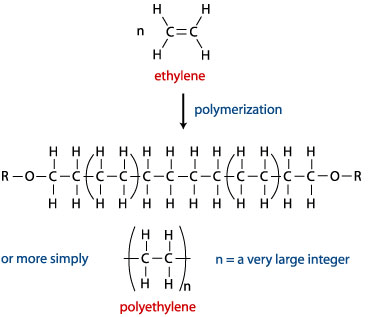
Other Polymers
Plastics are synthetic polymers. Polyethylene is a typical example of a polymer.
Leave a comment