- Introduction
- The structure of DNA, RNA and proteins
- The two types of RNA
- The genetic code
- Transcription
- Translation
Introduction
- DNA contains the genetic information needed to create proteins.
- Transcription is the process of converting that information into RNA.
- Translation is the process of using the RNA to create a protein.
The structure of DNA, RNA and proteins
- DNA, RNA and proteins are all polymers.
- The monomers in DNA are the bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine.
- The monomers in RNA are the bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil.
- The monomers in proteins are amino acids.
- DNA has two strands. One strand is used to code the genes. The other strand is used to duplicate the coding strand.
- The bases always associate in a specific way: adenine with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. (An easy mnemonic is that A & T both have only straight lines, and G & C have curves.)
The two types of RNA
- There are two main types of RNA: messanger RNA (mRNA) and transfer RNA (tRNA).
- mRNA is a long strand that mirrors the DNA that was used to make the mRNA.
- tRNA is a short strand of RNA that guides an amino acid into place on the developing strand of protein.
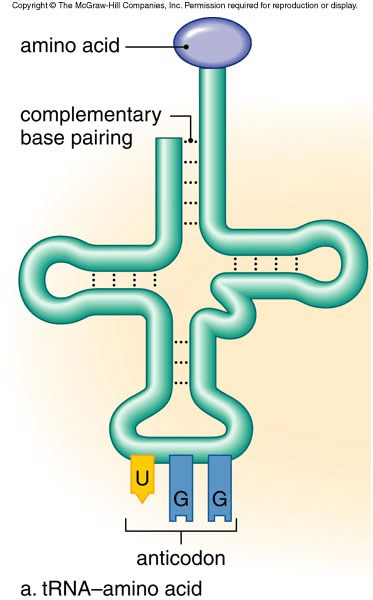
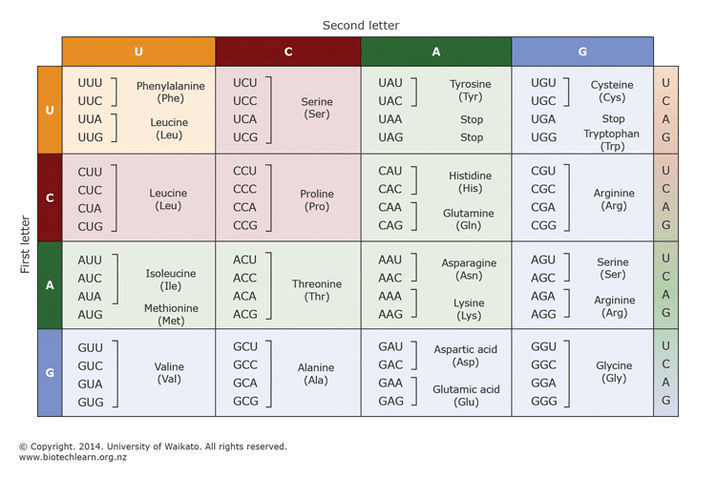
The genetic code
- There are only 4 bases in DNA, but there are 20 different amino acids used in proteins.
- Because of this, it takes 3 bases to code for one amino acid. The sequence of 3 bases is called a codon.
- However, DNA is not used directly to code proteins. Instead, DNA is used to make a strand of RNA which is then translated into a protein.
- Because RNA contains uracil instead of thymine, the genetic code is written with a U instead of a T.
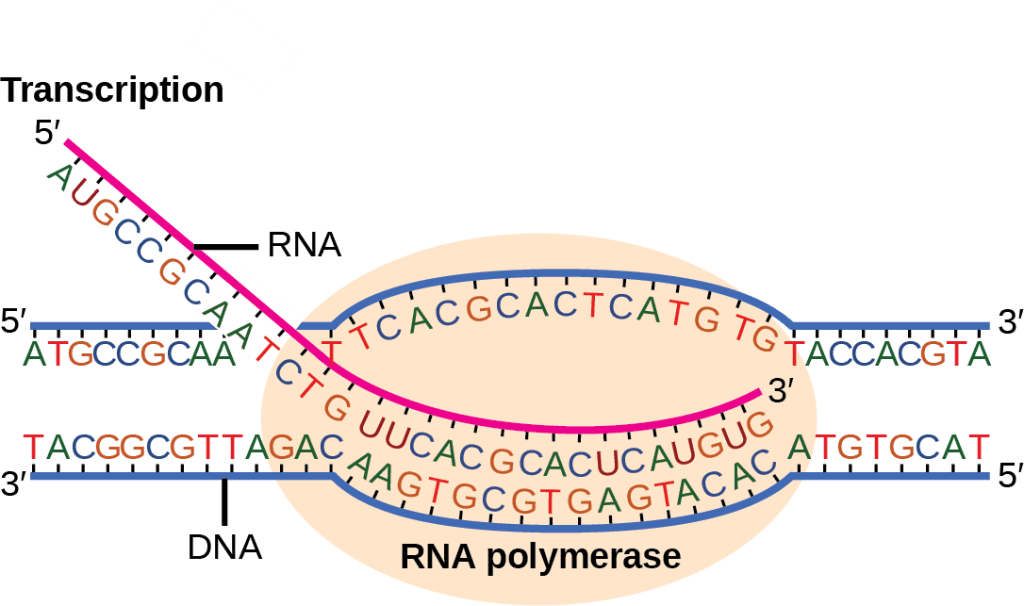
Transcription
- The coding strand of DNA is used to make a strand of RNA.
- On the DNA strand, an A (adenine) indicates a U (uracil) should be added to the RNA strand, a G (guanine) indicates a C (cytosine) should be added, a C indicates a G should be added, and a T (thymine) indicates an A should be added.
- This occurs in the nucleus of the cell.
Translation
- The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which uses the genetic code to translate the sequence of bases in the RNA into a sequence of amino acids in the protein.

Leave a comment