- Greek and Latin Roots
- Presentation Research Strategies
- Assignments
- Topics We Discussed This Week
- References
Greek and Latin Roots
Here is the list of Greek and Latin Roots for this week:
We will discuss these next week. Please bring your completed list next week.
Presentation Research Strategies
We discussed the 6 main “question words“.
We also discussed concept maps.
The topics that will be presented next week are:
- the atomic bomb
- skin
These are great topics, however, I strongly recommend narrowing the topic to be more specific.
Assignments
- Fill out the list of Greek and Latin roots.
- Write in the meaning of each root
- Give at least one example of each, be prepared to give its actual definition and the way that it is related to the root word
- Example: If I gave you the root “onym”, you could give the word “synonym” which has the definition of two words with the same meaning. The two roots in the word “syn” and “onym” mean “same name”, indicating two words that name the same thing.
- Fill out the blank space at the bottom with your own root that you have discovered. This will likely come from some of the example words that you have already written. Give a different example than what you have used.
- Example: syn- means “same”, example word “synchronous”
- Be prepared to talk about where you found this information
- Visit this page and write down the secret code, which is: “helium“
- Presentation
- Research your topic of choice and be prepared to give a 5 minute presentation on the topic, geared toward people your age level.
- Include the background information needed for someone who does not know the topic as well as you.
- Be prepared to talk about how you found this information.
Topics We Discussed This Week
Reading circuit diagrams
- Electronic symbols:
- Generator
- Battery
- Capacitor
- Resistor
- Transformer
- Diode
- LED
- Transistor
- Optical isolator
- Fuse
- Series and parallel circuits
- Tracing the path of the current

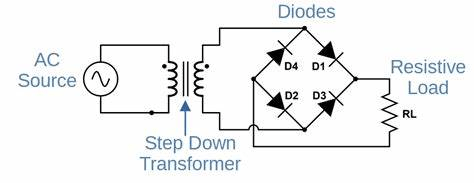
Direct current and alternating current
- DC comes from batteries
- AC comes from generators and is the form that is transmitted through power lines and is available at the outlet
- Many electronics use DC and therefore requires a transformer and AC to DC converter
- We examined a circuit of a bridge rectifier and discussed how it converts AC to DC.
Printed Circuit Boards
- We examined printed circuit boards (PCBs) and saw:
- The printed wires
- The words and symbols on the board indicating the components
- Through-hole boards and surface mounted devices
- Components:
- Capacitors
- Resistors
- Transformers
- Diodes
- Switches
- Variable resistors
- Microchips
- 7-segment LED display
Electric currents and magnetic fields
- A wire with an electric current has a magnetic field around it
- A changing electric field creates a changing magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field creates a changing electric field
- This is the basis for a transformer
- We saw how the LED on a computer power cord continued to glow due to the collapsing magnetic field.
Components
- We discussed the function of the following components:
- The concept of an optical isolator
- How a fuse works
- How a transformer works
- How a diode allows current to flow in only one direction
- How a capacitor works
Leave a comment