A “lingua franca” refers to a common language that is used by multiple groups of people who do not share a native language.
Wikipedia lists 73 languages that have been served as a lingua franca in some region of the world at some point in time. I want to focus on four.
Greek
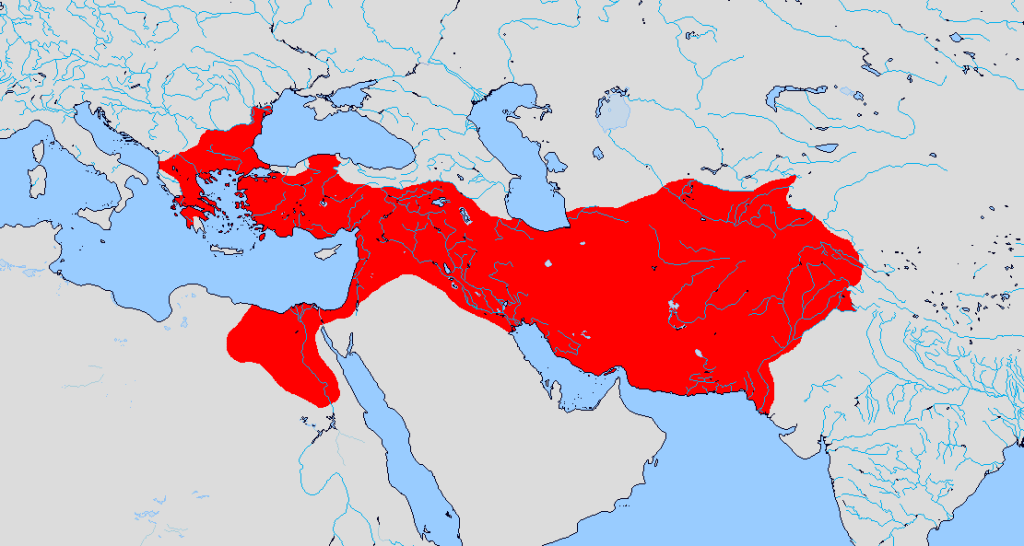
During the 4th century BC, the Greek king Alexander the Great established a relatively short-lived empire that stretched from the Middle East to India. It incorporated many cultures and many languages. Because the people with power over this region spoke the Greek language, it became the lingua franca of the region. Eventually it became the majority native language for people in many regions outside of Greece. Even after the Greek Empire was replaced by the Roman Empire in the Eastern Mediterranean, Greek was still commonly used. Famously, the New Testament was written in Greek, including the Paul’s letter to the church in Rome. After the Roman Empire was divided, the eastern half, known today as the Byzantine Empire, continued to use Greek as its lingua franca.
Latin
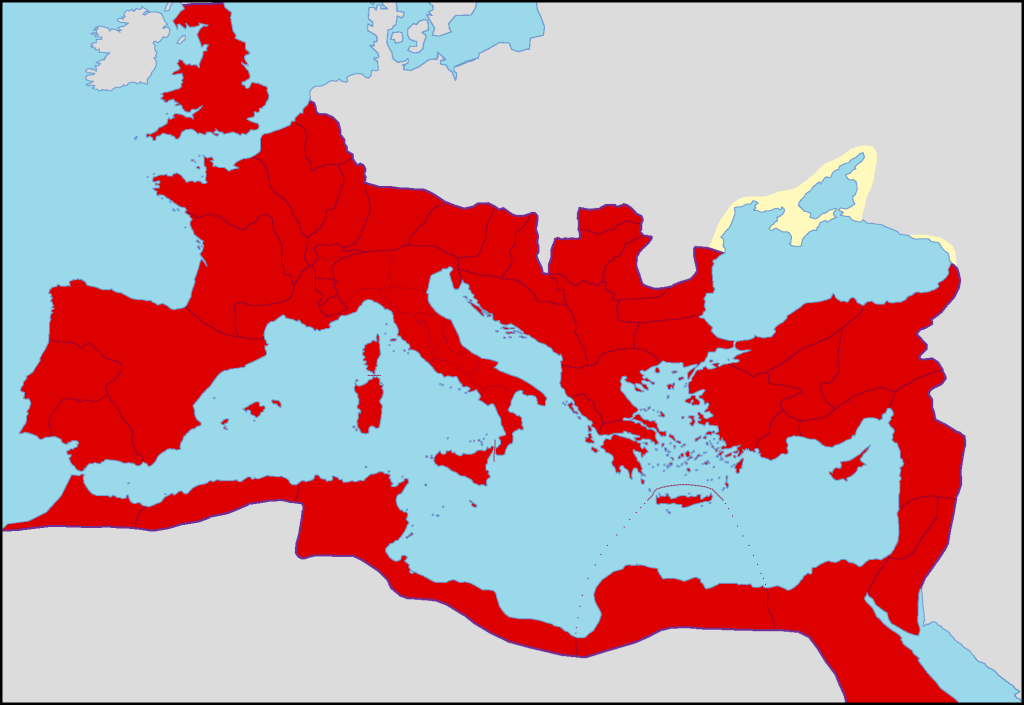
The Roman Empire controlled much of Western Europe for centuries. During this time, Latin was established as the lingua franca throughout the many cultures that were controlled by Rome. Native speakers of Celtic and Germanic languages had to learn Latin to communicate with their Roman rulers. Even though the western half of the Roman Empire fell in 476 A.D., Latin continued to be used as a lingua franca, especially among scholars, into the 19th century. Isaac Newton, for instance, wrote his famous 1687 work of physics, Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), in Latin.
Many of the major modern European languages, including French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, and Romanian, are descended from Latin. Even after there were no native speakers of Latin, the speakers of Romance languages could easily learn and use it as their languages are similar to Latin.
French
French has been used as a lingua franca for diplomacy since the 17th century. The International Olympic Committee and FIFA use it as their lingua franca. French colonization spread their language around the world and it is still in common use in many former French colonies, especially in Africa.
Although “franca” would seem to refer to France, in fact it refers to the Franks, a word used by people in the Middle East to refer to all people of Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The first lingua franca to be called by that name was a trade language used by sailors of the Mediterranean Sea beginning in the 11th century AD. Speaker of Coptic, Arabic, Syriac, and Greek used it as well as speakers of Romance languages like Italian and Spanish.
English
English is currently the world’s dominant lingua franca. Much of this is due to the spread of English by the former British Empire and the post-1945 dominance of the United States in world affairs, science and technology, and commerce. For instance, English is used by all international air traffic controllers. There are about 380 million native English speakers in countries once part of the British Empire. The United Kingdom, Ireland, Canada, the USA, Australia, and New Zealand are the countries were native English-speakers form a majority. However, English is commonly taught in schools around the world and there are over a billion people who speak it as a second language. Spanish and Chinese both have more native speakers than English does, but English is the most spoken language in the world.
Leave a comment