Greek and Latin Roots
Here is the list of Greek and Latin roots for this week:
Here is a link to all of the Greek and Latin roots we have discussed.
Greek and Latin Roots (There is a link to the Wikipedia page of Greek and Latin roots here, too.)
Test your memory of the Greek and Latin roots that we have discussed with this quiz.
ACT Prep
Lines
- The slope-intercept equation of a line: y = mx + b, is one of the most important equations in algebra, and shows up frequently and in many ways on the ACT test.
- In general, m is the slope of the line. The equation for the slope is the amount that the line goes up divided by the amount it moves to the right (“rise over run”).
- b is the y-intercept. This is what y equals when x is zero.
- Other forms of the equation include: y = mx (when the line crosses through the origin) and y = b (a horizontal line).
Tips
- Even if you are not familiar with some of the concepts or terms used in the question, you can often still figure out what makes senses.
- Watch out for different scales on the x- and y-axis.
- There are often multiple ways to approach a problem. You should use the approach that makes sense to you.
Presentations
You have all been doing a great job of learning about a new topic and discussing it in the group.
Great topics to research include:
- college and career options
- basic scientific concepts that you don’t understand
- how technology that we encounter in our everyday lives works
- science that underlies events in the news
The best topics are the ones that you are most interested in.
Presentations are meant to motivate you to be aware of concepts that you come across and to investigate them instead of ignoring them.
Assignments
- Fill out the list of Greek and Latin roots.
- Try the Greek and Latin roots quiz.
- Presentation
- Research your topic of choice and be prepared to give a 5 minute presentation on the topic, geared toward people your age level.
- Include the background information needed for someone who does not know the topic as well as you.
- Be prepared to talk about why you picked the topic and how you found information about it.
Next week we will meet on 7/31/24.
Things We Discussed
Greek and Latin roots
reti-
- endoplasmic reticulum

- reti- means “net”: retina, reticulated, retain
- reticulated giraffe


ec-, tom-, os-
- -ectomy = means “to cut out”: appendectomy, cholecystectomy, colectomy
- -ostomy = means “to cut an opening”: colostomy, ileostomy, tracheostomy
- -otomy = means “to cut”: lobotomy, craniotomy, thoracotomy, laparotomy
endo-, exo-
- endogenous refers to something “made or caused from within”
- exogenous refers to something “made or caused from outside”
- Examples:
| endogenous | exogenous | |
| tachycardia (fast heart rate) | due to bad electrical system in the heart | caused by hormones or drugs affecting the heart |
| depression | internal causes that make you depression even when circumstances are good | caused by a difficult situation in life |
| obesity | caused by genetics or hormones | caused by eating too many calories |
Orthopedic surgery
- An article about becoming an orthopedic surgeon
- Another option for people interested in taking care of athletes is a Sports Medicine fellowship after a Family Practice residency. They manage sports injuries but do not perform surgery.
MRI
- MRI stands for “magnetic resonance imaging”
- MRI is derived from technology called “NMR” which stands for “nuclear magnetic resonance”. NMR is used in organic chemistry to identify different chemicals.
Other imaging techniques include:
- X-rays
- CT scans
- Ultrasound
- Nuclear imaging
- PET scans
- HIDA scans
- Cardiac nuclear stress test
Receptors
Titan implosion
- An explosion occurs when pressure builds up inside a container until the container cannot hold the pressure and the container bursts apart. A strong container is needed for a big explosion because it allows the pressure to build higher.
- In the same way, an implosion occurs when pressure on the outside is so much stronger than the inside that the container collapses.
- In the case of a submersible, the strongest container is a sphere. This can be seen in pictures of early submersibles:

Spheres have much more resistance to collapse than a cylinder does.
- In the case of the Titan, it likely collapsed at a pressure that it had previously been able to tolerate because it was built with inferior materials which gradually weakened with each dive that it took.
Secondary metabolites
- Primary metabolites are chemicals produced by living organisms that are essential for their growth and reproduction.
- Secondary metabolites are chemicals that are needed only because of their interaction with their environment, usually decreasing them from being eaten (by tasting bad or being poisonous), but sometimes by protecting them from extreme temperatures, UV radiation, etc.
- Secondary metabolites can be organized into groups based on the metabolic pathways that are used by the organism to produce them.
- In plants, the major groups of secondary metabolites are:
- terpenes
- alkaloids
- glucosinolates
- phenols
- A key learning point is to recognize that a two-word phrase may represent an important concept that cannot be understood by understanding each word separately. You should be on the lookout for this.
Learning strategies
This diagram demonstrates how a single concept can bring together many different concepts that you already know. In this example, the red circles illustrate the new knowledge I learned and the black represents concepts I already understood:
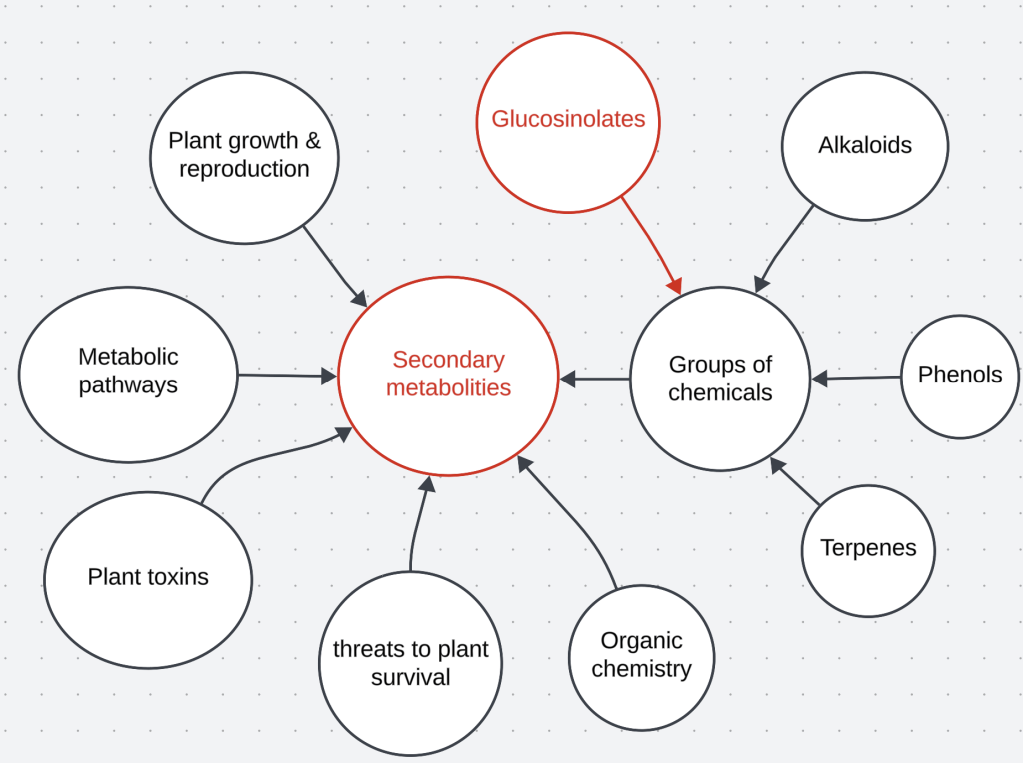
As you learn more about a variety of concepts, you develop a network of understanding that allows you to make more and more connections.
This is a better concept than the concept of a solid circle of knowledge that is expanding as you learn:

Hopefully, the idea of your knowledge being an interconnected network will motivate you to find ways to connect new information to the knowledge you already have, rather than dismissing it because your knowledge circle hasn’t expanded to reach the new knowledge yet.
Leave a comment