Meaning: different, other
Root word: Greek ἕτερος (héteros) meaning “one or the other of two”
Similar roots: all- meaning “other”
Opposite roots: hom- meaning “same”, ortho- meaning “straight”
Derived English Words
Commonly encountered words are in bold.
Heterochromatin: A form of chromatin that is densely packed and generally not actively transcribed. It plays a role in gene regulation and maintaining chromosome structure.
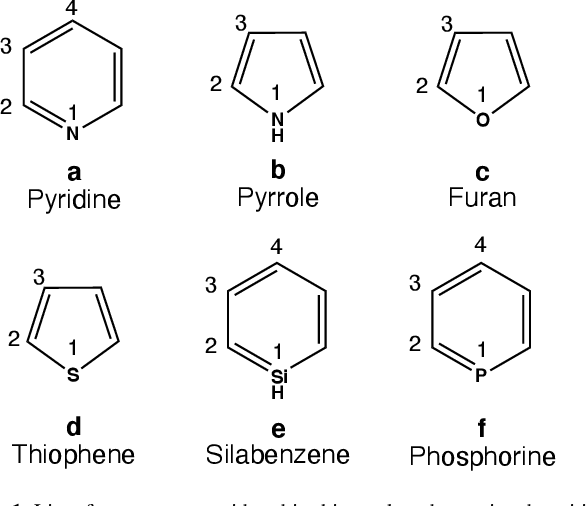
Heterocyclic: Referring to a type of chemical compound that contains a ring structure with at least one atom that is not carbon (such as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur)
Heterodox: Referring to beliefs or opinions that diverge from established or accepted standards, especially in religion or philosophy.
Heterodoxy: The quality or state of being heterodox; beliefs or doctrines that differ from the accepted norms.
Heterogeneity: The quality or state of being diverse in character or content; a mixture of different elements or components.
Heterogeneous: Composed of different or diverse elements; not uniform in composition or character.
Heteronuclear: Pertaining to molecules that consist of different types of atoms
Heteronym: A word that is spelled the same as another word but has a different meaning and usually a different pronunciation. For example, “lead” (to guide) and “lead” (a type of metal).
Heterophil: An organism or cell that exhibits a preference for different forms or types; often used in biological contexts to describe species that thrive in diverse environments.
Heterophile: A term used to describe a person who has a preference for or attraction to individuals of different types or characteristics, particularly in the context of sexual orientation, culture, or social interactions. In some contexts, it can refer to someone who is open to or embraces diversity in relationships or friendships.
In a scientific context, heterophile often refers to organisms or cells that have a preference for or are attracted to different types of stimuli or environments. This term can be used in various fields, such as biology or ecology, to describe organisms that thrive in diverse conditions or that engage with a range of different species.
Heterophilic: Referring to the attraction or affinity for different species or types; in biological contexts, it often describes organisms or cells that interact or react with different types of cells or organisms. This term can be used in various fields, including immunology, where it may refer to antibodies that recognize antigens from different species, or in ecology, describing interactions between different species.
Heterophobia: An irrational fear or aversion to individuals who are different in some way, particularly in terms of sexual orientation or gender identity.
Heterosexuality: A sexual orientation characterized by attraction to individuals of the opposite sex.
Heterosexual: A person who is attracted to individuals of the opposite sex.
Heterotopic: Referring to tissues or organs that are located in an abnormal position within the body

Heterosis: The phenomenon where hybrid offspring exhibit superior qualities or traits compared to their parents, often seen in agriculture and animal breeding.
Heterotic: Pertaining to or resulting from heterosis; often used to describe traits or phenomena that arise from hybrid vigor.
Heterozygote: An organism or cell that has two different alleles for a specific gene, one inherited from each parent. For example, in a gene that has two variants (alleles), A and a, an individual with one A allele and one a allele would be considered a heterozygote (Aa). Heterozygotes can exhibit a variety of traits depending on whether the alleles are dominant or recessive. This genetic diversity can have implications for traits, health, and adaptability in populations.
Heterozygous: A genetic term describing an organism that has two different alleles for a specific gene, one inherited from each parent; this can lead to variations in traits.
Links
List of Greek and Latin roots in English – Wikipedia
Other Roots Used in These Words
- chrom-
- cycl-
- dox-
- gen-
- nuc-
- nym-
- phil-
- phob-
- top-
- -osis
- zyg-
Leave a comment