Meaning: flesh
Root word: Greek σάρξ, σαρκός (sárx, sarkós)
Roots with similar meanings:
- corp– meaning “body”
- soma– meaning “body”
Roots with opposite meanings:
- spir– meaning “spirit, breathe, wind”
Roots that could be confused:
- sacr– meaning “sacred”
Notes: Many structures found in all cells, such as the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum, have names specific for muscle cells, such as the sarcoplasm and the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Derived English Words
Commonly encountered words are in bold.
Perisarc: The outer covering or protective layer of certain protozoa and some other organisms.
Sarcasm: The use of irony to mock or convey contempt; a sharp or cutting remark.
Sarcastic: Marked by or given to using sarcasm; often intended to mock or convey contempt.
Sarcocele: A swelling or tumor of the flesh, typically referring to a tumor of the testicle.
Sarcoid: Referring to a type of granulomatous inflammation that resembles sarcoma; can refer to lesions in certain diseases.
Sarcoidosis: An inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of granulomas in various organs, particularly the lungs and lymph nodes.
Sarcoma: A type of cancer that arises from connective tissues, such as bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, or blood vessels.
Sarcophagus: A stone coffin, often elaborately decorated, used in ancient times for burial.
Sarcoptes: A genus of parasitic mites belonging to the family Sarcoptidae. The most well-known species is Sarcoptes scabiei, which causes scabies in humans and many other animals. These mites burrow into the skin, leading to intense itching, inflammation, and the formation of rashes. Sarcoptes mites are typically transmitted through close physical contact and can infest both humans and animals.
Sarcoptiform: Relating to a group of microscopic arachnids (like mites) characterized by a body structure similar to that of sarcoptes.
Sarcopterygii: A class of fish known as lobe-finned fishes, which have fleshy, lobed fins and are considered ancestral to tetrapods.
Sarcoplasm: The semi-fluid substance that fills the spaces between the myofibrils in muscle fibers, involved in muscle contraction.
Sarcoplasmic: Pertaining to the sarcoplasm, the cytoplasm of muscle cells, which contains stored glycogen and myoglobin.
Sarcolemma: The cell membrane surrounding a muscle fiber, which plays a crucial role in transmitting electrical signals necessary for muscle contraction.
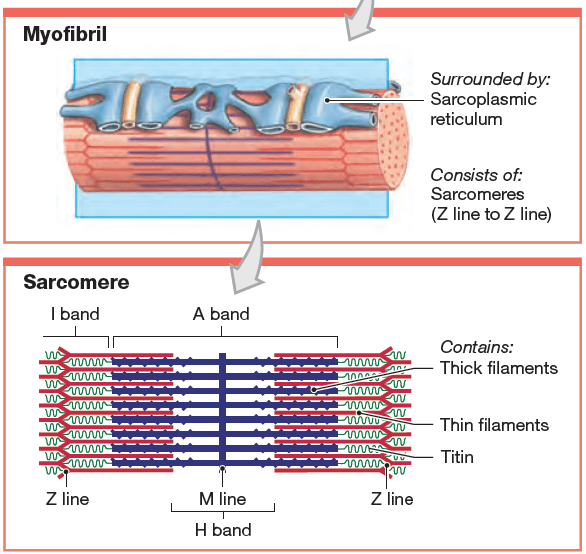
Sarcomere: The basic structural and functional unit of striated muscle tissue, responsible for muscle contraction. It is the segment of a myofibril bounded by two Z discs (or Z lines) and contains the overlapping filaments of actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments). When a muscle contracts, the sarcomeres shorten as the actin filaments slide past the myosin filaments, leading to overall muscle shortening and force generation. Sarcomeres are arranged in series along the length of myofibrils, giving skeletal and cardiac muscles their striated appearance.
Sarcosome: A cellular organelle involved in muscle metabolism, related to energy production in muscle cells.
Sarcopenia: The loss of muscle mass and strength that occurs with aging.
Sarcosine: An amino acid derivative that occurs naturally in the body and is involved in various metabolic processes.
Sarcosinemia: The presence of sarcosine in the blood, often studied in relation to certain metabolic conditions.
Links
List of Greek and Latin roots in English – Wikipedia
Other Roots Used in These Words
| -cele | swelling |
| em- | blood |
| -form | shape |
| -oma | tumor |
| -penia | deficiency |
| peri- | around |
| plas- | to shape or mold |
| phag- | eat, swallow |
| pteryg- | wing |
| soma- | body |
Leave a comment