You can find a list of posts from previous science clubs here.
Greek and Latin Roots
Here is the list of Greek and Latin roots for this week:
Here is a link to all of the Greek and Latin roots we have discussed.
Test your memory of the Greek and Latin roots that we have discussed with this quiz.
This is the link to the Wikipedia list of Greek and Latin roots.
Things We Discussed
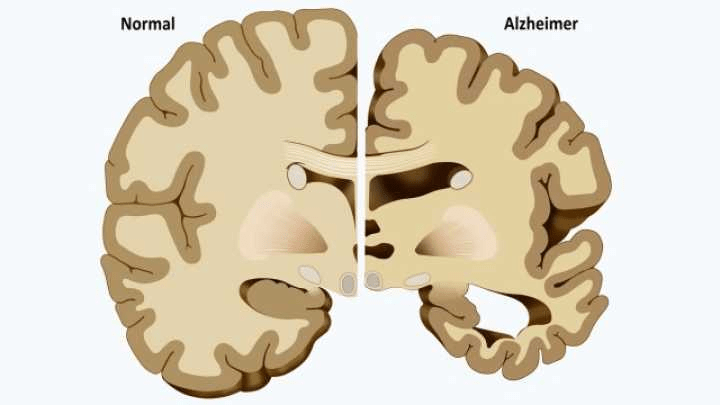
Alzheimer’s Dementia
- There are multiple aspects to memory:
- Recent memory
- Older memories (episodic memory)
- Facts learned (semantic memory)
- How to do tasks (implicit memory)
- Alzheimer’s dementia affects recent memory much earlier than it affects other types of memory.
Skull Growth
- Babies has soft spots and unfused skull bones in order to make room for their brains to grow, which continues until about age two when their skull bones fuse.

- The brain of a young adult completely fills the skull

- As we age and brain cells die, our brains get smaller. This is called atrophy. Dementia makes this much worse. Even though our brains get smaller, the skull does not, leaving room between the brain and skull (which is filled with cerebrospinal fluid).

Measuring Gas Collected with a Load Cell
Here is a detailed description of my experiment:
Determining the kinetics of carbon dioxide production by yeast
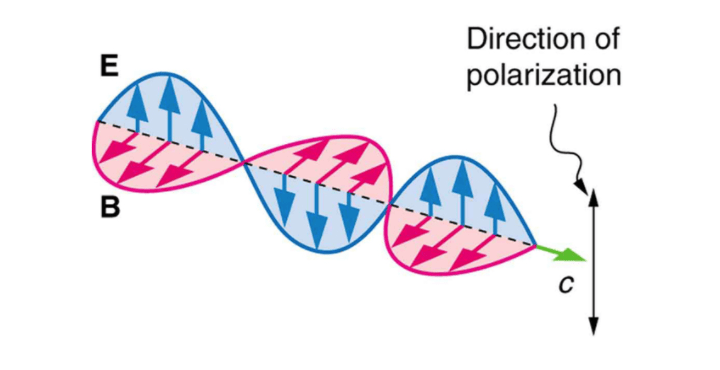
Electromagnetic waves
- Light is an electromagnetic wave.
- It has an electric field which oscillates in a plane (represented by E) and a magnetic field (B) which oscillates in a plane perpendicular to the electric field.
Polarized Light
- Light emitted from most sources is unpolarized, so the electric fields can be oriented in any direction.
- However, a polarizer will only allow light through that is polarized in one direction.
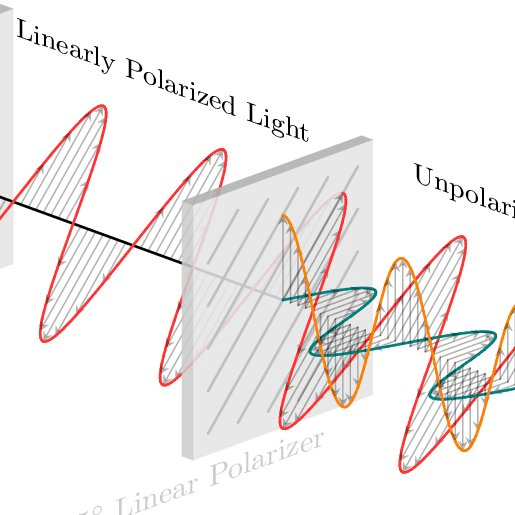
- When two polarizers are aligned, the second polarizer allows the same light through that the first one did. But when the second polarizer is rotated 90 degrees, it blocks the light that the first polarizer let through.
- Some objects (especially some crystals) rotate the polarization of the light that passes through it.
- This means that polarized light that goes through the object will be able to pass through another polarizer that is not aligned with the first polarizer.
- Because the crystals rotate different frequencies of light by different amounts, we see more of one color than another.
Polarized Light Microscopy
- Microscopes can be fitted with two polarizers so that we can look at samples with polarized light.
- This is a technique that is often used in geology (because rocks are made of crystals), but also in biology and chemistry.
Crystals Photographed with Polarization Microscopy – The Canadian Nature Photographer
Other Forms of Microscopy
This link contains images produced by different microscopy techniques:
Microscopy images (Basic science review)
Here is a quiz to test your recognition of different microscopy techniques:
Things To Do
- Fill out the list of Greek and Latin roots.
- Determine the roots in the example word.
- Write in the meaning of each root.
- Give at least one example of another word that shares the same root, be prepared to give its actual definition and the way that it is related to the root word.
- Presentation
- Research your topic of choice and be prepared to give a 5-minute presentation on the topic, geared toward people your age level.
- Include the background information needed for someone who does not know the topic as well as you.
- Be prepared to talk about how you found this information.
Next time we will meet on 2/13/25.
Leave a comment