
What is mass?
Mass is the quantity of matter in an object. Matter, on the other hand, is anything that has mass and takes up space. Since an object’s volume can change, mass is the way we measure how much matter is in the object.
Mass is typically measured by the amount of force that the mass experiences in a gravitational field. This force is what we call the object’s weight. However, unlike weight, the mass of an object does not change whether it is measured on the Earth, Moon, Mars, or some other gravitational field.
What is volume?
Volume is the 3-dimensional measure of how much space is being occupied by the matter.
What is density?
Density is the concentration of matter. It is analogous to when we calculate the concentration of a solute dissolved in water. We would calculate the concentration of 3 grams of salt dissolved in 2 L of water in the same way, as the mass divided by the volume.
When it is not otherwise specified, density refers to the concentration of matter in a volume. However, in certain situations, density can deal with area or even a linear measure. For instance, population density measures the number of people per square mile. You could also measure the density of cars on the road as cars per mile.
What are m and v?
m represents mass and v represents volume. This can be seen by comparing the formula in words with the formula in symbols, and recognizing the obvious connection between m and mass, and v and volume.
What is ρ?
The lowercase Greek letter rho, ρ, is the standard symbol for density. There is no particular way to connect ρ to the concept of density. You just have to know that ρ is representing density. However, by comparing the formula in words with the formula in symbols, you can match ρ with density.
You should take care not to confuse ρ with the Greek equivalent of a Latin p, which is the Greek letter pi, π.
What are kg and m3?
kg represents kilograms, a common unit of mass. m3 represents cubic meters, a common unit of volume. kg is a single unit. You must recognize that this is not k times g. On the other hand, m3 is a derived unit indicating meters times meters times meters.
You must also recognize that the m representing mass and the m in m3 represent two very different things.
You should also understand the difference between base units and derived units.
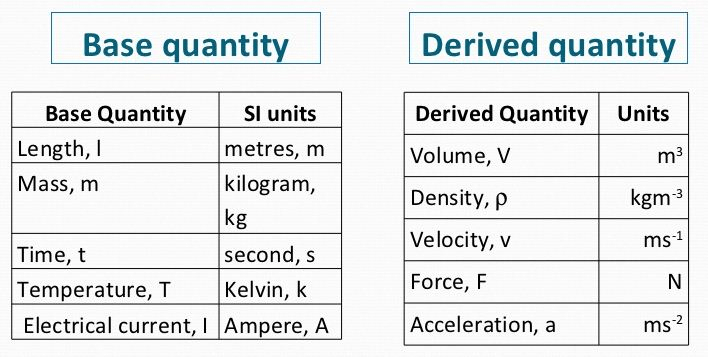
Finally, you must recognize that although density is always the mass divided by volume, the mass and the volume may be in different units. Common units for density include g/mL, g/L, kg/L, g/cm3, etc.
What do the green circles in the cube represent?
They represent the orderly arrangement of closely packed atoms in a solid.
What is wrong with this illustration?
The illustration sets quantities (m/v) equal to units (kg/m3). This is a common mistake which can lead to confusion.

The proper way to distinguish the concepts of quantity and unit when writing is to use brackets, [ ], around the quantity.

If you took this equation as a literal algebraic equation, you could rearrange it to get v = m4/kg. This is meaningless nonsense, the result of the “abuse of the equal sign” as it is known.
Leave a comment