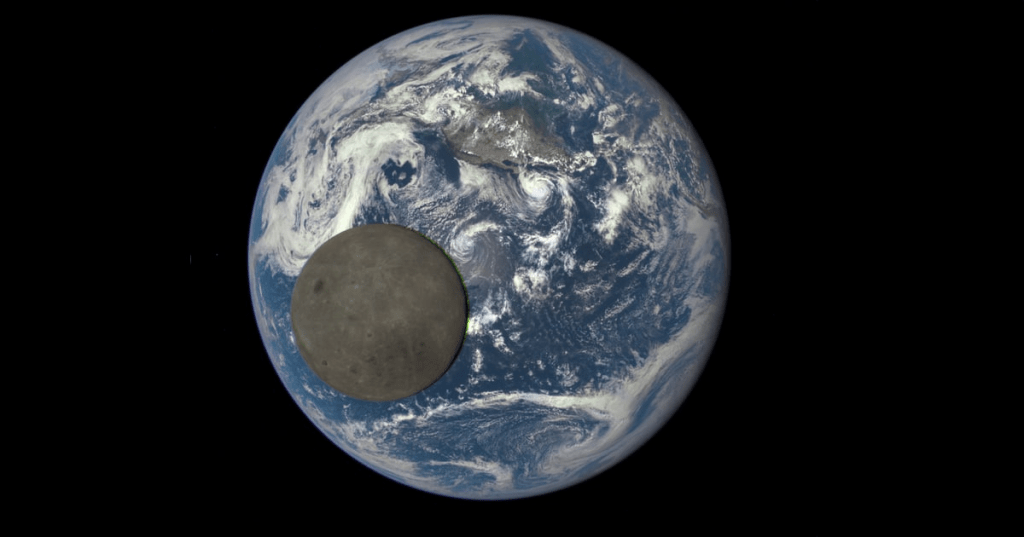
What is this?
The moon in front of the Earth.
Why does the moon look different than we normally see it?
The same side of the moon is always facing Earth, so this image shows the far side of the moon.
Where is the sun relative to the Earth and moon in this image?
Behind and to the left of the camera.
If the sun were not behind the camera, part of the Earth and moon would be in shadow. In fact, you can see a little bit of the terminus (the dividing line between light and dark) of the moon in the lower right, which indicates the sun is a little to the left.
Which direction would you expect the moon to move over time?
Up and to the right
The moon orbits the Earth in the same direction that the Earth turns. The orbit of the moon must be in the same plane as the center of the Earth.
Where is the North Pole?
In the upper left corner of the Earth
What land mass can you identify?
Baja California, Mexico, and the western United States
What ocean is the moon over?
Pacific Ocean
What time of year was this taken?
Summer
There are two tropical storms visible over the ocean in the Northern Hemisphere and very little snow visible on the Rocky Mountains or Arctic. Most importantly, the North Pole is tilted toward the Sun and fully illuminated.
What can you say about the distance from the Earth that this picture was taken?
It was taken a long way from the Earth.
If the camera were close to the Earth, it would be very close to the moon and the moon would look relatively bigger compared to the Earth. In actuality, the moon’s diameter is about 1/4th the diameter of the Earth.
Assuming the camera didn’t move relative to the Earth, what land mass would appear in subsequent images?
The Earth rotates toward the east, so Asia and/or Australia would be seen next.
Assuming the camera didn’t move relative to the Earth, how long would it take for the moon to pass in front of the Earth?
Several hours
This is how long a lunar eclipse takes.
It will take a point on the Earth about 12 hours to cross from one side of the planet to another. The moon revolves around the Earth slower than the Earth rotates, so you might think that it would take longer than a few hours, but the moon would spend most of the time in its monthly orbit to one side of the Earth or the other and not directly in front or behind the Earth.
What does the relative brightness of this image indicate about the brightness of the Earth?
In this image, the Earth is significantly brighter than the moon. Yet, from the camera’s viewpoint, the moon is illuminated like a full moon. Therefore, in actually, the Earth is brighter than a full moon.
The fraction of light that is reflected by an astronomical body is called the albedo. Earth’s albedo is about 0.4, while the moon’s albedo is about 0.15. So, Earth reflects about 2.5 times as much of the light that hits it as the moon does.
Goals of this image:
- Recognizing features of the Earth
- North Pole
- Continents
- Oceans
- Weather patterns
- Recognizing clues to seasons
- Tropical storms
- Snow cover
- Tilt of Earth relative to the Sun
- Relative sizes and positions in the solar system
- Lighting as a clue to the Sun’s position
- The effects of distance on relative sizes
- Rotation vs. Orbital movements
References
From a Million Miles Away, NASA Camera Shows Moon Crossing Face of Earth – NASA
Leave a comment