- Science-related Events
- Greek and Latin Roots
- Important Points We Discussed
- Details of Things We Discussed
- Things To Do
- Footnotes
You can find a list of posts from previous science clubs here.
Science-related Events
Here is a link to upcoming science-related events in mid-Missouri. I try to update this each month.
Greek and Latin Roots
Here is the list of words with Greek and Latin roots for this week:
Here is a link to all of the Greek and Latin roots we have discussed.
Test your memory of the Greek and Latin roots that we have discussed with this quiz.
This is the link to the Wikipedia list of Greek and Latin roots.
Important Points We Discussed
Chemical bonds
- There are two main types of chemical bonds: ionic and covalent bonds
- Ionic compounds dissolve in water by splitting into ions
- Covalent bonds do not break when a compound dissolves in water.
- The type of bond is determined by the relative electronegativities of the atoms involved.
- The number of bonds that an element can make is determined by which column of the periodic table it is in.
- From left to right on the periodic table, the elements form 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0 bonds.
- Carbon and nitrogen can form double or triple bonds, oxygen can form double bonds.
Statistical significance
- Some apparent relationships within data are due to coincidence.
- Relationships are only considered to be statistically significant when they are unlikely to occur by chance.
- The threshold that is usually used to define statistical significance a probability that a relationship occurred by chance of less than 1 in 20.
- This probability is known as the p-value.
- Statistical significance is often indicated by p < 0.05.
- The number of combinations of heads and tails in n trials is 2n.
EKGs
- EKGs show the electrical signal of the heart.
- An EKG can be used to see the rate, rhythm and shape of the signal.
- The natural pacemaker of the heart is called the sinus node.
- The natural pacemaker fires independently.
- The signal passes through the atria first and then to the ventricles through the AV node.
- The path of the signal from the atria to the ventricles is reflected in the pattern of the EKG.
- The P wave represents the atrial contraction.
- The QRS complex represents the ventricular contraction.
Details of Things We Discussed
Book Recommendation
The Hot Zone by Richard Preston
Planning College Classes
Requirements for a College Degree
In general, there are 3 types of requirements for a college degree:
- general education classes – everyone has to take history, English, math, science, etc.
- major-specific classes – if you are a biology major, you are expected to take a lot of biology classes
- total credit hours – typically around 120 credits. If your general education and major-specific classes don’t add up to the total credit hours required, then you need to take extra classes of your choosing. These are called electives.
Pre-Med Students
Pre-med students are students that plan to go to medical school after college. There is not a pre-med major. Instead, you can have any major and still get in to medical school as long as you take the classes that the medical school expects you to. However, it typically works best to have a major that also expects you to take a lot of the same classes.
Majors that are common for pre-med students are biochemistry, chemistry, and biology.
Mizzou Biology Major Semester Plan
BS in Biological Sciences | University of Missouri Academic Catalog
Example of Classes Recommended Before Applying to Medical School
Chemical Bonds
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of the relative strength with which an atom attracts an electron in a bond.
Electronegativity is largely determined by the charge on the nucleus and the distance that the electron is away from the nucleus. Since the charge of the nucleus gets larger as you move to the right in the periodic table but the outer shell stays the same until you drop to the next row of the periodic table, electronegativity gets larger as you move to up and to the right on the periodic table. Fluorine has the highest electronegativity.

Number of Bonds that an Atom Will Form
As a general rule, the smaller atoms, particularly the first 20, form bonds by either giving up an electron from its outer shell or gaining an electron. The elements in the first column of the periodic table have one electron in the outer shell which they can give away, giving it a +1 charge. The elements in the second column can give away 2 electrons, giving them a +2 charge.
On the right side of the periodic table are the noble gases. They have complete outer shells, do not tend to gain or lose electrons and typically do not form bonds with other atoms. The column just to the left of the noble gases have outer electron shells that are just one electron short of being full and they are happy to accept an electron, which gives them a -1 charge.
The electrons in the outer shell that can be gained or lost are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons that are involved in a chemical bond.
Atoms form bonds by losing or gaining electrons in the outer electron shell to make a complete outer shell. The number of bonds that atoms form is determined by the number of electrons that they want to gain or lose. This is shown on the periodic table below, as the green or red numbers above each column. The absolute value of this number (lose the + or – sign) gives the number of bonds that the atoms in that column can form. So, from left to right, the number of bonds is 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0.1

Double and Triple Bonds
Some elements are able to form double and triple bonds.
Carbon can form double or triple bonds.
Nitrogen can also form double or triple bonds.2
Oxygen only has 2 bonds, so it can only form a double bond.
Isomers
A chemical formula shows how many atoms of each element are in a compound. For a given chemical formula, there may be more than one way to put the atoms together. Isomers are compounds are made of the same atoms but put together in different ways.
An example of isomers is acetic acid and glycoaldehyde, which both have a chemical formula of C2H4O2. In each diagram, carbon is represented as black, oxygen is red, and hydrogen is white.


EKGs
Most of the information that we discussed about EKGs is explained in a previous post: Rhythm strips
Things To Do
- Fill out the list of Greek and Latin roots.
- Determine the roots in the example word.
- Write in the meaning of each root.
- Give at least one example of another word that shares the same root, be prepared to give its actual definition and the way that it is related to the root word.
- Presentation
- Research your topic of choice and be prepared to give a 5-minute presentation on the topic, geared toward people your age level.
- Include the background information needed for someone who does not know the topic as well as you.
- Be prepared to talk about how you found this information.
Footnotes
- The Group B elements are metals. These metals are different because they can start filling outer shells before their inner shells are full. The number of bonds that they can form is not as easy to predict as the smaller atoms. In fact, the number of bonds they can form is not a fixed number. For example, copper can bond to oxygen to form copper (I) oxide, Cu2O, and copper (II) oxide, CuO. ↩︎
- A great example of a triple bond is hydrogen cyanide, which has a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen.
↩︎
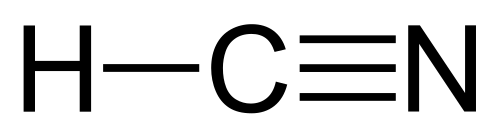
Leave a comment